In Python, like in all programming languages, data types are used to classify one particular type of data. This is important because the specific data type you use will determine what values you can assign to it and what you can do to it (including what operations you can perform on it).
In this tutorial, we will go over the important data types native to Python. This is not an exhaustive investigation of data types, but will help you become familiar with what options you have available to you in Python.
Data types in Python
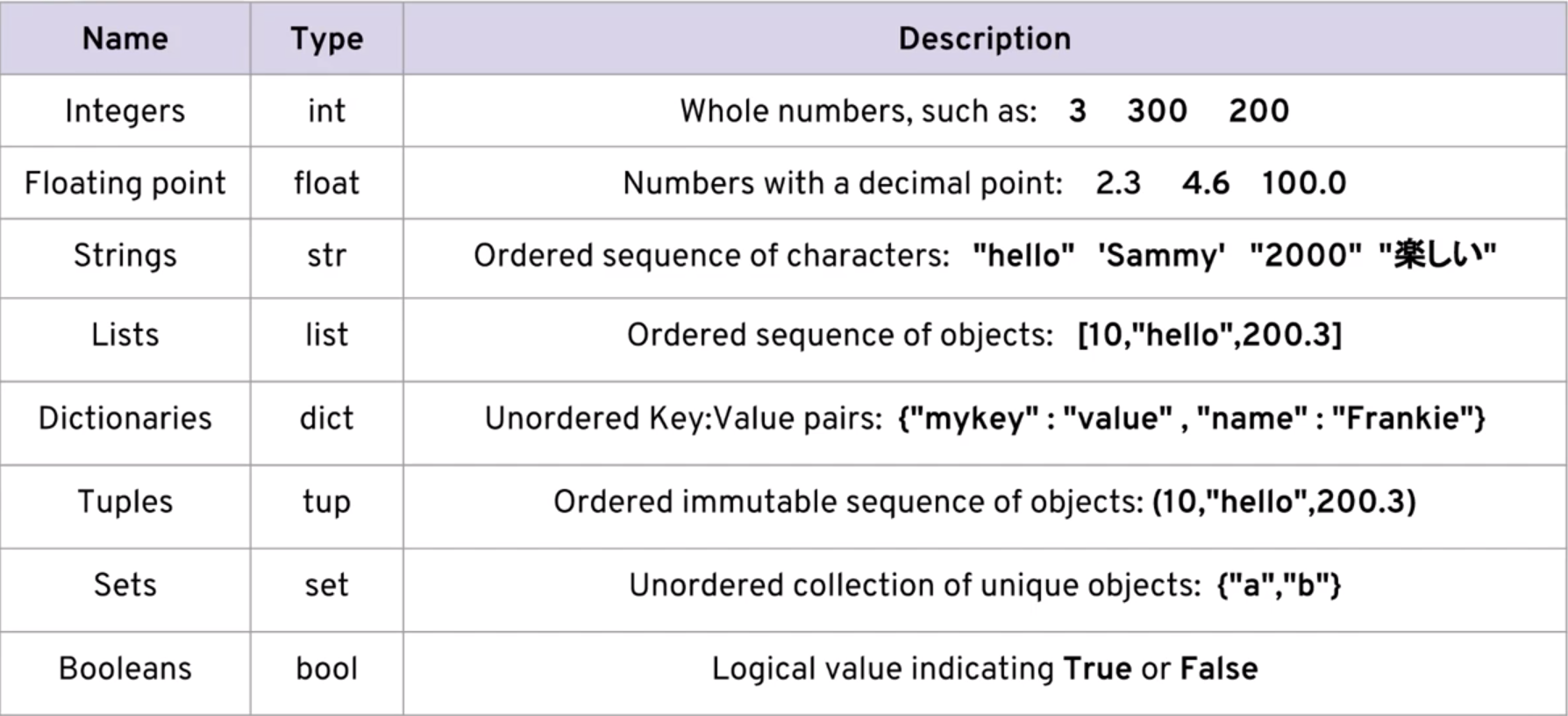
Every value in Python has a data type. Since everything is an object in Python programming, data types are actually classes, and variables are instance (object) of these classes.
There are various data types in Python. Some of the important types are listed below
- Python Numbers
- Python List
- Python Tuple
- Python Strings
- Python Set
- Python Dictionary
- Python boolean
- Log in to post comments